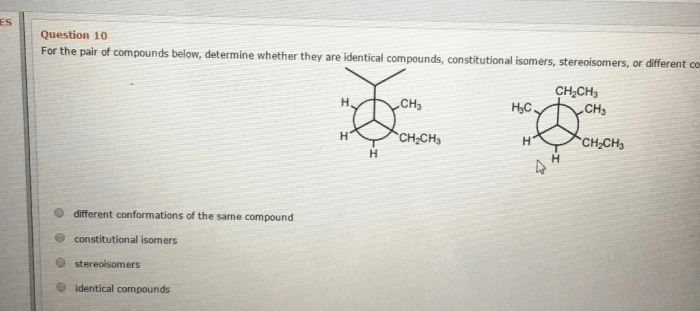
Determine whether the following compounds are constitutional isomers – Constitutional isomerism, a fundamental concept in chemistry, emerges as a captivating realm where compounds share the same molecular formula yet exhibit distinct molecular structures. Embark on an exploration of this intriguing phenomenon, deciphering the intricacies that differentiate constitutional isomers and unraveling their significance in shaping the chemical landscape.
Delving deeper into the topic, we will establish a systematic approach for determining constitutional isomers, unraveling the interplay between molecular formula and structural formula. Through illustrative examples, we will discern compounds that embody constitutional isomerism and those that stand apart.
Constitutional Isomerism

Constitutional isomerism refers to the phenomenon where compounds with the same molecular formula possess distinct molecular structures and connectivity of atoms. These isomers differ in the arrangement of their atoms, leading to unique chemical and physical properties.
Determining Constitutional Isomers
To determine whether compounds are constitutional isomers, follow these steps:
- Compare the molecular formulas of the compounds. If they differ, they cannot be constitutional isomers.
- If the molecular formulas are the same, draw the structural formulas of the compounds.
- Identify the connectivity of atoms in each structural formula. If the connectivity is different, the compounds are constitutional isomers.
Examples and Applications
| Compound 1 | Compound 2 |
|---|---|
| Butane | Isobutane |
| Ethanol | Dimethyl ether |
Constitutional isomerism plays a crucial role in drug design, where slight variations in molecular structure can significantly alter biological activity.
Advanced Concepts, Determine whether the following compounds are constitutional isomers
Resonance can introduce additional complexity to constitutional isomerism. Resonance structures represent different electronic configurations of a molecule that contribute to its overall structure. Compounds that exhibit resonance may have multiple constitutional isomers, depending on the arrangement of double bonds and lone pairs.
Essential Questionnaire: Determine Whether The Following Compounds Are Constitutional Isomers
What is the key difference between constitutional isomers and stereoisomers?
Constitutional isomers differ in their molecular connectivity, while stereoisomers have the same molecular connectivity but differ in their spatial arrangement.
How can I determine if two compounds are constitutional isomers?
Compare their molecular formulas and structural formulas. If they have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas, they are constitutional isomers.
What are some examples of constitutional isomers?
Butane and isobutane, pentane and neopentane, and 1-propanol and 2-propanol are all pairs of constitutional isomers.